Inflation is a Continuing Decline in the General Level of Prices of Goods and Services
- Inflation is a situation of rising prices in the economy.
- A more exact definition of inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level in an economy.
- Inflation means an increase in the cost of living as the price of goods and services rise.
- The rate of inflation measures the annual percentage change in the general price level.
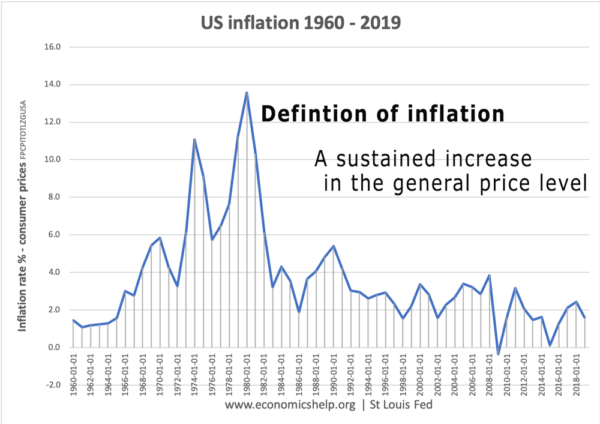
Inflation and value of money
- Inflation leads to a decline in the value of money. "Inflation means that your money won't buy as much today as you could yesterday."
- If the prices of goods rise. the same amount of money will purchase a smaller quantity of goods.
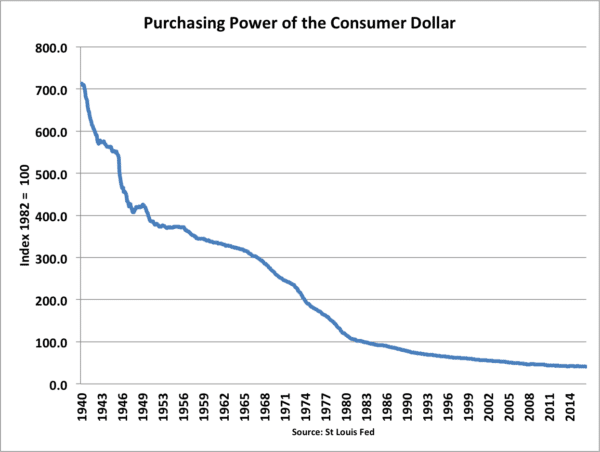
This diagram shows how inflation in the US has eroded the purchasing power of the dollar. The biggest decline in the purchasing power of the dollar occurred in the 1970s when inflation was highest.
Purchasing power of the Pound Sterling (1920=100)
| 1920 | 1930 | 1940 | 1950 | 1960 | 1970 | 1980 | 1990 | 1998 |
| 100 | 125 | 129 | 98 | 66 | 46 | 133 | 6.8 | 5.33 |
This table shows us that £100 buys fewer goods in 1998 than 1920, (approx 78% of its value)
Types of inflation
- Cost-push inflation – when a rise in prices is caused by a rise in the cost of production, such as higher oil prices
- Demand-pull inflation – when a rise in prices is caused by rising aggregate demand and firms pushing up prices due to the shortage of goods
Definition Hyper-Inflation
Hyperinflation is generally considered to occur when inflation is greater than 1000%. With hyperinflation, money loses its value so rapidly that nobody wants to use it as a medium of exchange.
In 1920s Germany had inflation of 100 billion %
In 1946 Hungary had inflation of 42,000 billion per cent
See: Hyperinflation
Graph showing UK inflation rate
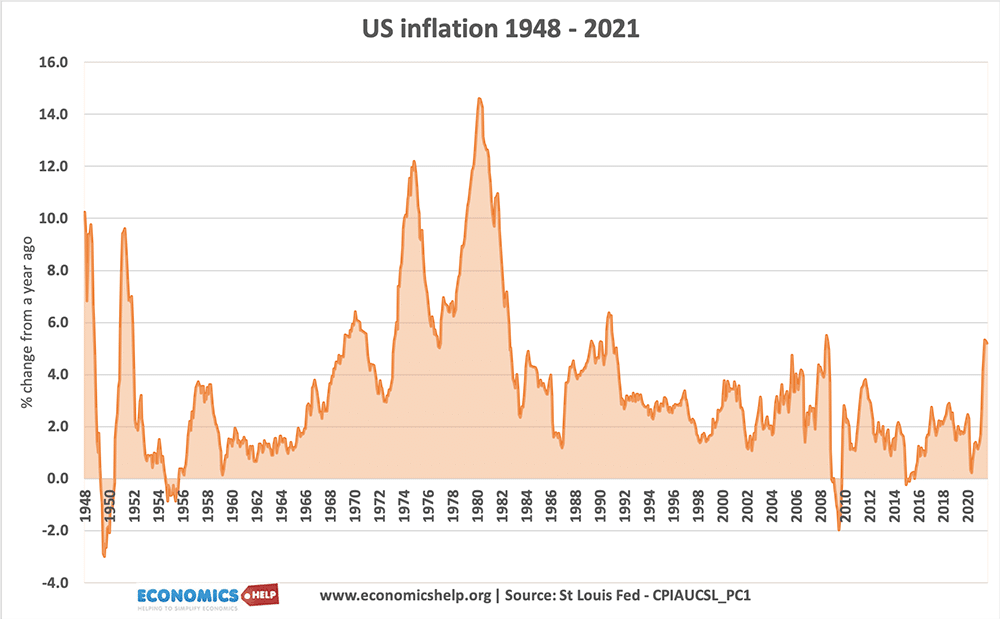
UK inflation in the post-war period.
- In 1974, the inflation rate peaked at 25%. This was due to rising oil prices and rising wages.
- In the late 1990s and early 2000s, the inflation rate fell to less than 2% in 2004.
- This fall in the inflation rate means prices were increasing at a slower rate.
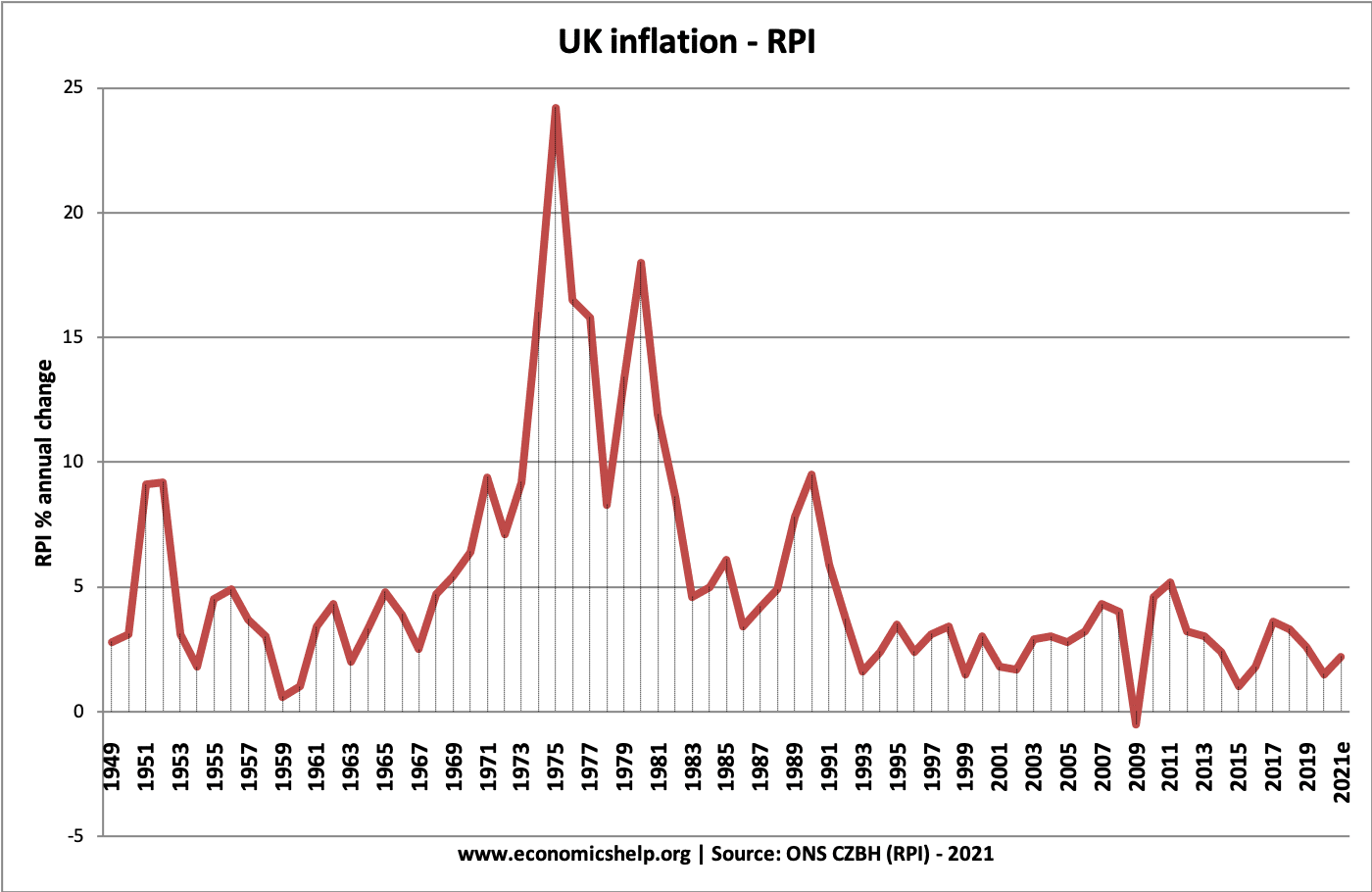
UK Inflation since 2008
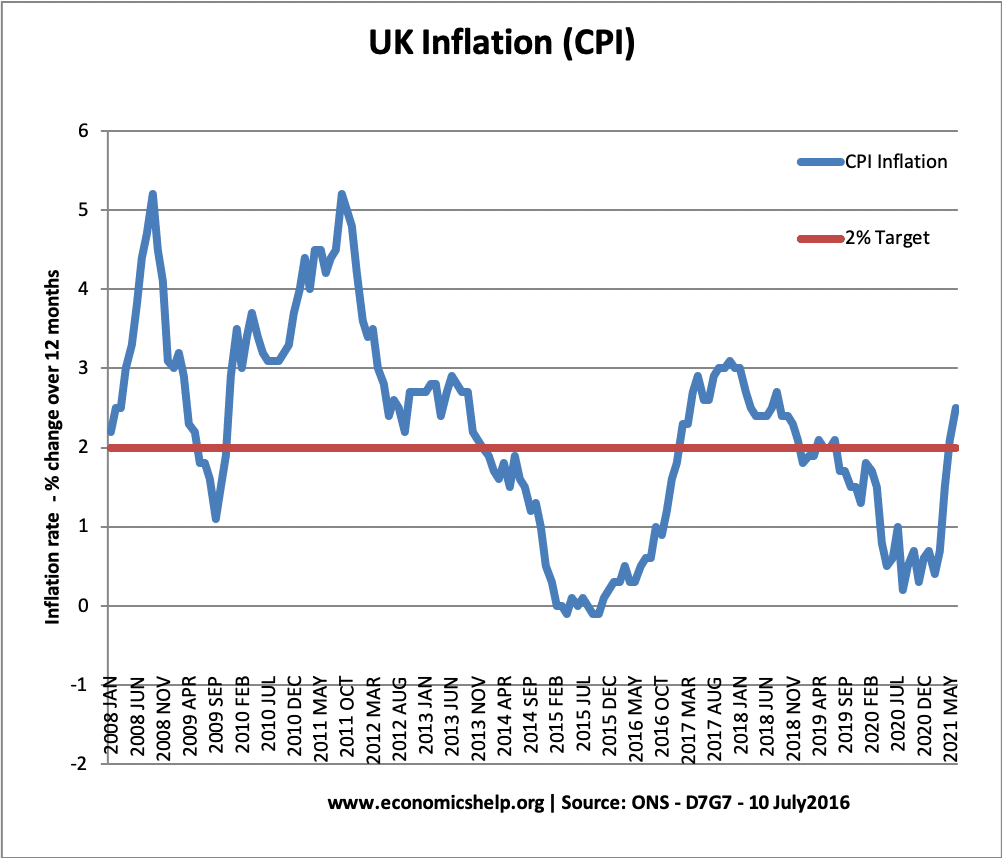
- Inflation was close to the government's target of 2% between 2000-2007
- In 2008, inflation peaked at 5%, primarily because of a surge in the price of oil.
- Inflation fell in 2009, because of the recession and fall in demand.
- In mid-2015, there was a short period of deflation (negative inflation rate – falling prices)
Definition of Deflation
Deflation is a fall in the price level of the economy. It means there will be a negative inflation rate.
See more on deflation
Measuring inflation
To calculate inflation, the statistics authority (ONS)
- Measure the price of 1,000 goods every month
- Gives a weighting to different goods depending on how important they are in a typical basket of goods.
- An index is created with calculates the weighting of good * price change.
See more on Measuring inflation
Costs of inflation
Inflation is seen to have economic costs. These include:
- A decline in value of savings
- Uncertainty for business leading to less investment.
- A decline in the competitiveness of exports (if inflation higher than in other countries.)
See also: Costs of inflation
Causes of inflation
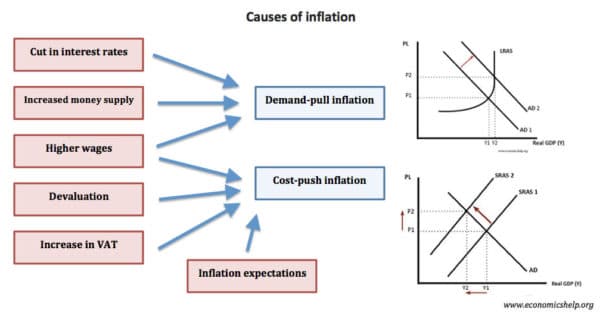
Inflation can be caused by:
- Excess demand. Rapid economic growth causes firms to put up prices
- Rising costs. For example, rising price of oil/commodities causes rise in price of goods.
See also: Causes of inflation
Related
- Inflation – advantages and disadvantages
- Different types of inflation
- Historical Inflation Rates for more details
You can read more at our privacy page, where you can change preferences whenever you wish.
buntonjuserebeaven.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.economicshelp.org/macroeconomics/inflation/definition/